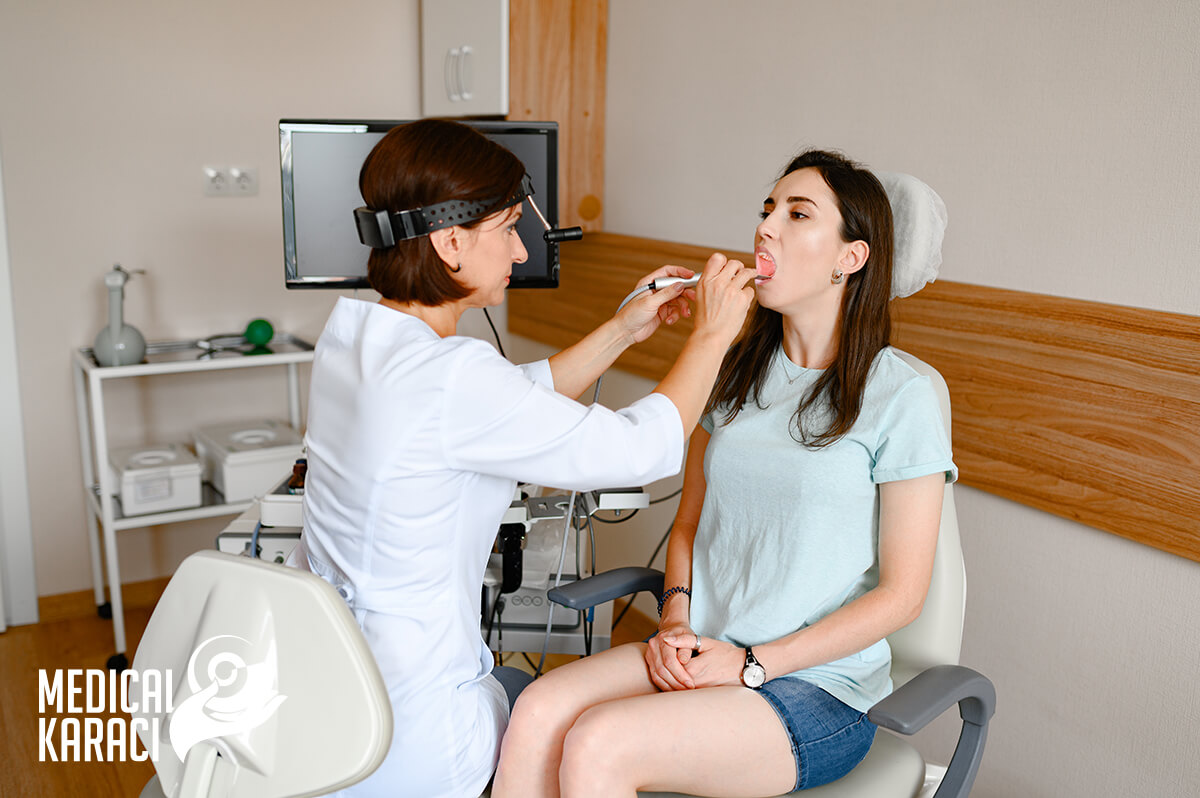
Otorhinolaryngology or Ear, Nose and Throat (abbreviated ENT) is the medical field that studies the origin, development, treatment and prevention of diseases of the ears and nasopharynx.
These organs belong to 3 different functional systems - nervous, respiratory and digestive. Their crossing at the base of the head determines their morphological unity. The close proximity of the tissues is a serious prerequisite for the rapid spread of disease processes between them. Many diseases proceed simultaneously in 2 or more of the systems, which makes it necessary to treat them by the same specialist.
Otorhinolaryngology has 2 main areas:
- Otology - studies ear diseases and hearing disorders. Otology has a well-defined, independent section.
- Otoneurology - studies the diseases of the balance-hearing apparatus and neurological disorders of hearing. Otoneurology is a very essential section of military, aviation and aerospace medicine.
- Rhinolaryngology - studies diseases of the nose, paranasal sinuses and nasopharynx.
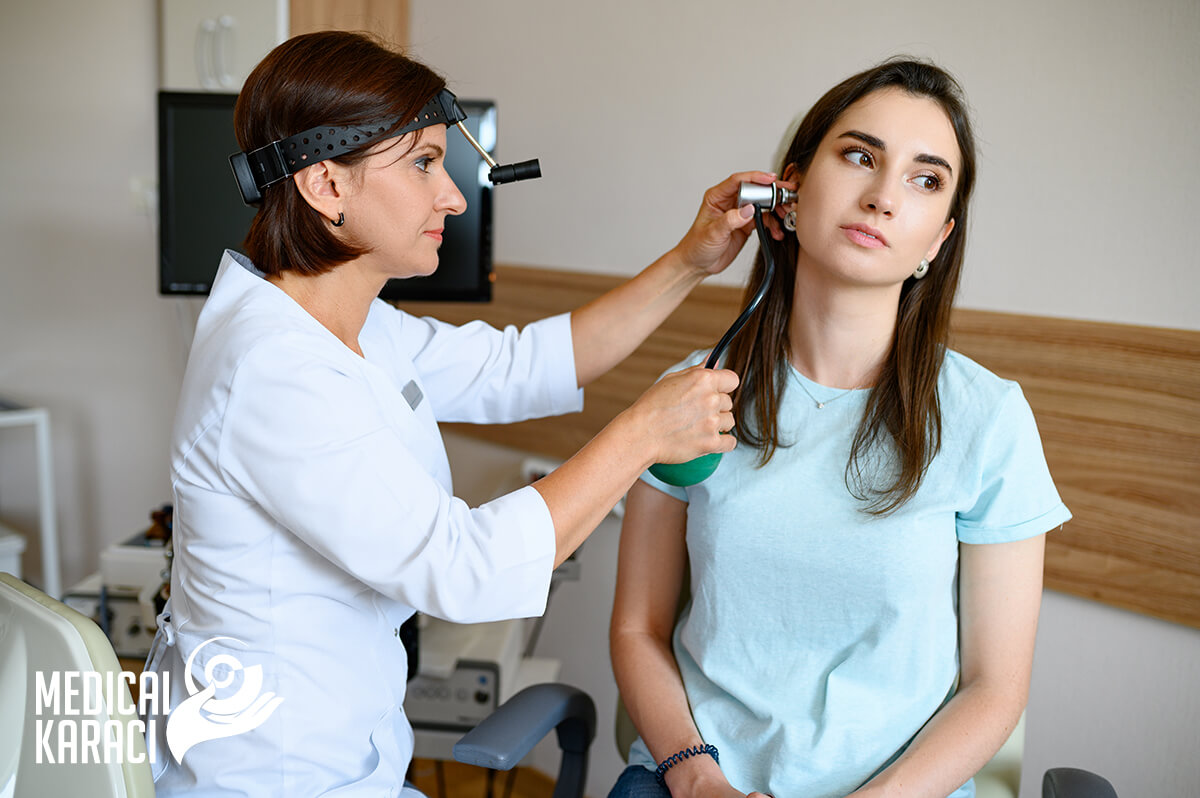
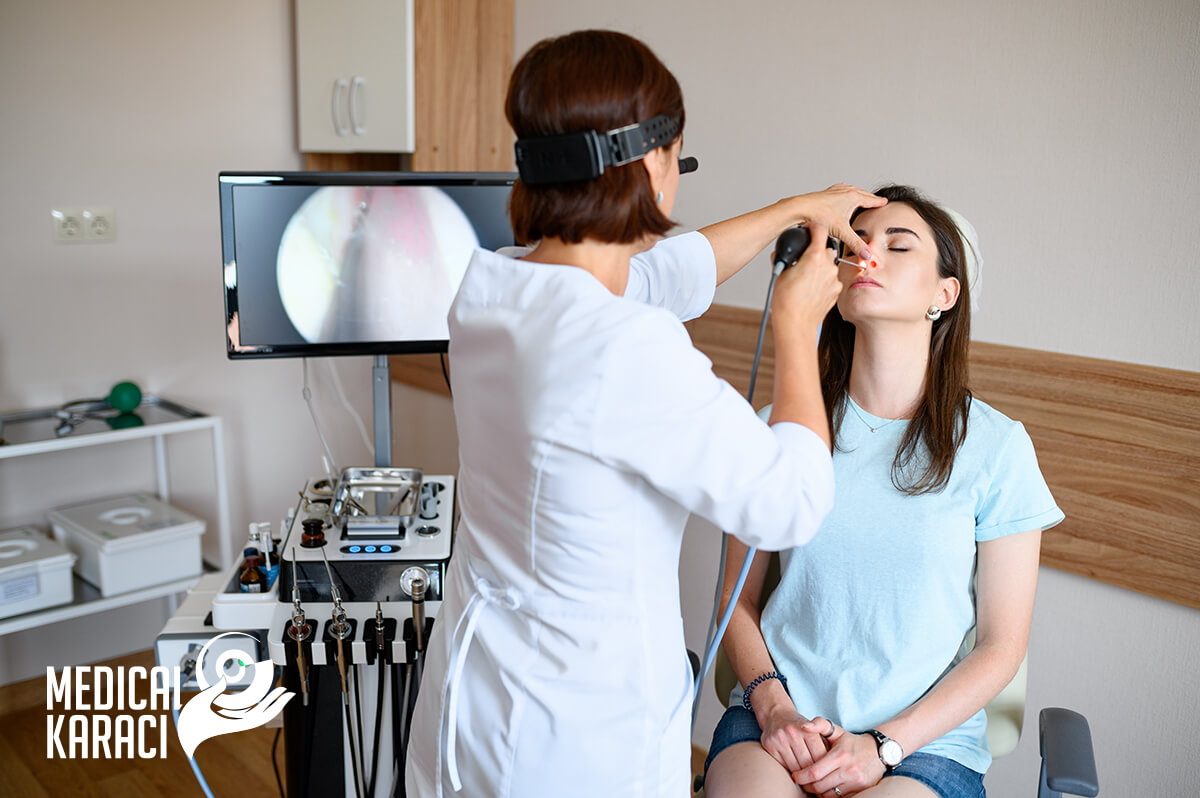
Consultative examinations, rhinoscopy, otoscopy and audiometry are performed in the Ear, Nose, Throat (ENT) rooms. Ear, Nose, and Throat specialists perform competent evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of the organs of the head, neck, and especially the face, nose, sinuses, throat and pharynx, larynx, ears, and organs at the base of the skull. ENT doctors deal with problems of hearing, smell, swallowing, speech, facial musculature and balance caused by disease, injury or hereditary defects.
The Ears, Nose and Throat division deals specifically with:
- Diagnosis and treatment of ear diseases:
- Acute and chronic diseases: otitis in children and adults
- Tinnitus
- Disturbances in balance
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the nose:
- Acute and chronic diseases: rhinitis, sinusitis, allergic diseases
- Difficulty in nasal breathing: distorted nasal septum, nasal polyps, concha hypertrophy
- Diagnosis of snoring by endoscopic examination of the upper airway during induced sleep and polysomnography, and treatment by laser uvulopalatoplasty or radiofrequency thermotherapy
- Conservative treatment of the sinuses: cysts, facial neuralgias, sinusitis of dental origin
- Aesthetic and functional corrections of the nose - rhinoplasty
- Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the throat:
- Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the throat and larynx
- Benign and malignant formations of the larynx and trachea
- Acute and chronic diseases of the tonsils: tonsillitis (angina), tonsillar abscesses, pharyngitis
- Inflammatory processes of the neck
- Acute and chronic diseases of the larynx: voice disorders, laryngitis, laryngotracheitis, subchordal laryngitis
- Operative treatment of ear-nose-throat diseases:
Endoscopic, bloodless surgeries for ear disorders such as acute and chronic otitis, eardrum perforations, cholesteatoma, hearing enhancement surgeries.
Methods of hearing testing:
Audiogram
The audiogram is a graph that illustrates the patient's hearing used and the degree of hearing loss the patient has for each ear.
During the study, the audiologist presents sounds of a certain frequency at a given time. The lowest tone that a person can hear for a particular frequency is recorded in the audiogram for that frequency and loudness, as a threshold of hearing sensitivity.
An audiogram shows how much your hearing differs from the norm and if hearing loss is reported, where the cause may be. If you have a hearing impairment the audiologist will recommend an appropriate solution.
Audiometry
It is a hearing test. A painless and non-invasive test that determines a person's ability to hear different sounds - their intensity /loudness/ and pitch.
The results of audiometric tests are used to diagnose the cause of hearing loss, or ear disease. It is used as routine screening for early detection of hearing disorders.
During the audiometry are performed:
- Tonal audiometry with pure tones - the lowest tone the patient can hear is determined. At this time he wears headphones and hears a series of tones directed to one ear and then the other ear. He will be asked when he hears a sound to press a button or otherwise signal. The results of the test are automatically recorded and presented in the form of an audiogram. A device called a bone oscillator is then placed on the bony process behind each ear and used to examine bone conduction.
- Speech audiometry - assesses a person's ability to distinguish speech from background noise.
- Tympanometry - identifies problems such as fluid build-up, earwax or a perforated eardrum.
For more information, you can call +359895770869.