The specialty of cardiology covers the diagnosis and treatment of all diseases of the cardiovascular system, and also includes heart defects, inflammatory diseases of the heart muscle and heart linings, arterial hypertension, heart rhythm disorders, congenital heart defects, and much more.
Cardiology is a branch of internal medicine.
Cardiologist and cardiac surgeon are 2 separate specialties.
- The cardiac surgeon opens the chest and performs heart surgery.
- The cardiologist specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Heart disease refers specifically to the heart, while cardiovascular disease affects the heart, blood vessels, or both.
Symptoms that may signal a heart problem include:
- shortness of breath / shortness of breath
- dizziness
- chest pain
- changes in heart rate or rhythm
- high blood pressure
The cardiologist may conduct tests for heart murmur or abnormal heart rhythm.
Cardiologists treat patients who have had a heart attack, have heart failure (HF) or other heart problems. They have an essential role in making decisions about heart surgery (heart surgery), heart catheterization, angioplasty, and stenting.
Here are some of the major heart diseases:
- atherosclerosis
- atrial fibrillation (AF)
- arrhythmias
- congenital heart disease
- coronary heart disease
- congestive heart failure
- high blood cholesterol and triglycerides
- hypertension
- pericarditis
- ventricular tachycardia
- high blood pressure or hypertension
A person may need to see a cardiologist even without symptoms if, for example, they have a family history of heart disease or high cholesterol, if they are or have been a smoker, if they have diabetes.
Cardiologists may perform or refer the patient to perform the following tests:
- ECG: recording the electrical activity of the heart
- Stress test: it shows the heart rate changes with rest and exercise. It measures the work and limitations of the heart.
- Echocardiography: can measure how well the heart is pumping blood. The test can detect inflammation around the heart, known as pericarditis. It can also identify structural abnormalities or infections of the heart valves.
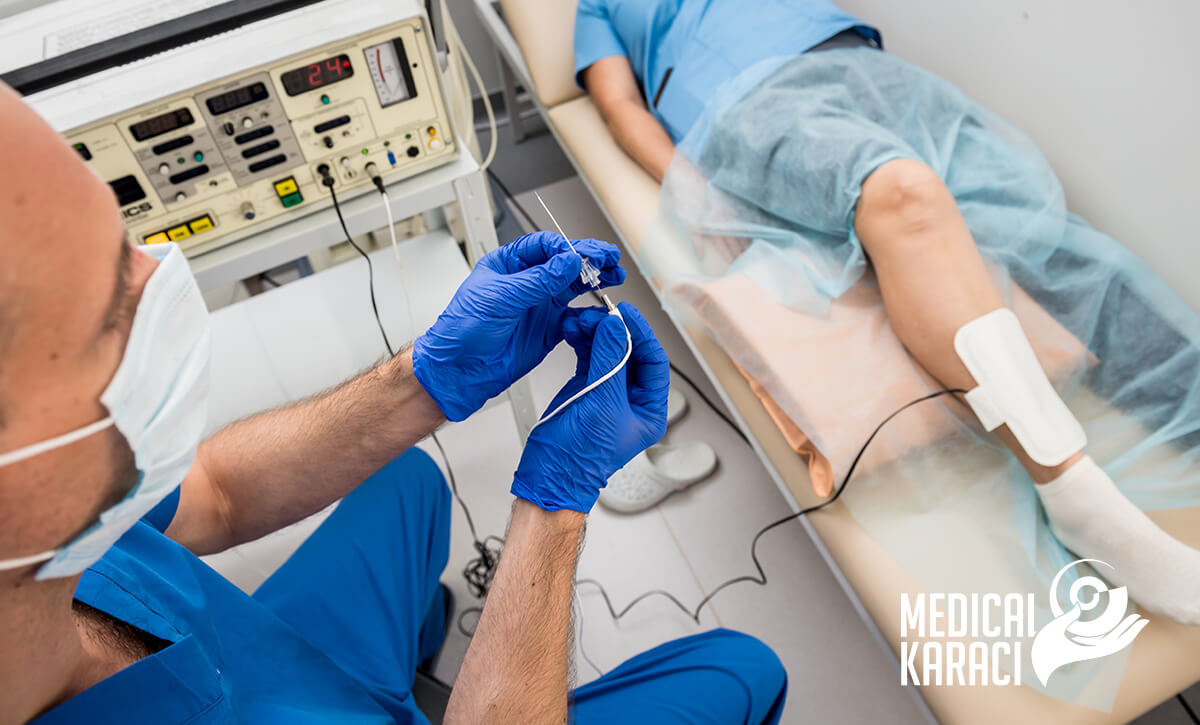
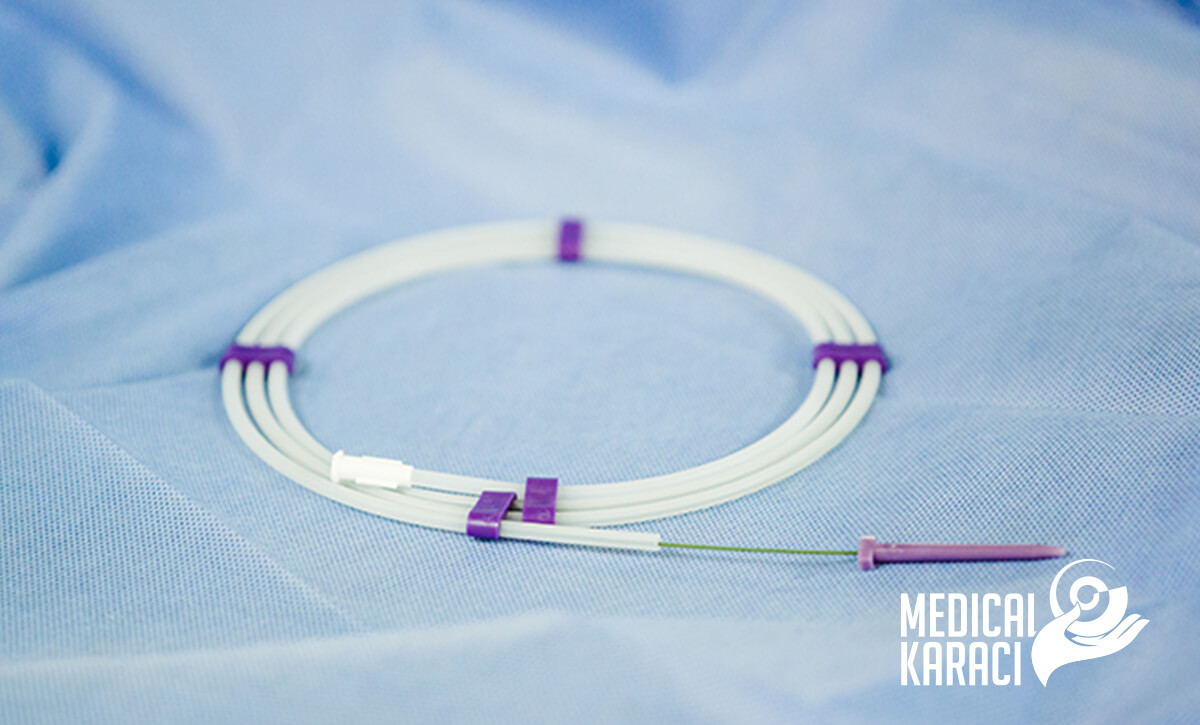
- Cardiac catheterization: is an invasive procedure - a small catheter is inserted through a blood vessel in the arm or leg and reaches a heart chamber or coronary blood vessel. It can take pictures and check the function of the heart. The procedure is used to diagnose and treat congenital heart, valve and coronary disease. Apart from cardiac catheterization, other procedures performed are- coronary angiography, ventriculography.
- Nuclear cardiologyA: Nuclear imaging technologies use radioactive materials to study cardiovascular disorders and diseases in a non-invasive way.
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology is a subspecialty of cardiology.
The physician electrophysiologist conducts a so-called EFI (Electrophysiological study). This is an invasive study of the electrical activity and conduction of the heart that gives important information about possible arrhythmias. The electrical activity is measured by introducing catheters with electrodes that carry out the measurement.
Catheter ablation is another procedure the Electrophysiologist undertakes.
The pacemaker "PM" and the implantable cardiac device "ICD", also known as an implantable cardioverter defibrillator, are small electronic "devices" used to correct abnormal heart rhythms. Your doctor may suggest one if you have had at least one bout of abnormal heart rhythm.
Pacemaker implantation - PM identifies and coordinates the contractions of the heart muscle so that the heart beats efficiently. This is accomplished by sending precisely sensed electrical signals to correct certain abnormalities in the heart rhythm.
Aortocoronary bypass
This is a type of surgical operation that achieves restoration of blood flow to the heart muscle and preserves its vital pumping function. The operation is performed in ischaemic heart disease when there is stenosis of the coronary vessels feeding the heart muscle.
In coronary bypass surgery, the narrowing of the blood vessels is preserved by creating a bypass route for which different arteries and veins - grafts - can be used.
The graft connects on one side to the aorta or a large branch of it and enters the coronary artery after the site of narrowing or blockage.
The operation is performed under general anaesthesia using extracorporeal circulation. A so-called heart-lung machine is used to ensure the movement of blood and its oxygenation during the time when the heart is temporarily stopped.
The vessels with which the bypass will be carried out shall be prepared in advance. Usually the left and right internal thoracic arteries, the radial artery of the arm, the saphenous vein of the leg are used.
After opening the chest, the aorta is clamped, and a cold solution with a high potassium content is infused into its root, which temporarily stops the heart from working. During this time, the previously prepared grafts are connected, thereby bypassing the narrowing of the vessels and restoring blood flow. Normal cardiac activity is restored and the patient is removed from anaesthesia.
The postoperative period requires gentle physical activity and avoidance of heavy physical loads that make the heart work harder.
The use of an extracorporeal circulation device is associated with a decrease in the body's defences and a risk of infection.
Angioplasty
Angioplasty, accompanied by vascular stenting, is applied to narrowed and blocked arteries in the human body.
- Narrowing of the large arteries of the human body /aorta and its major branches/ covered by aretosclerosis and calcification.
- Peripheral vascular diseases, representing narrowing of the vessels of the hands and feet.
- Renal hypertension.
- Diseases of the carotid arteries, narrowing of the arteries of the neck supplying blood to the brain.
- Coronary artery disease, affecting the arteries of the heart that supply oxygen to the heart muscle.
- Narrowing of the central venous vessels, in some cases their stenting.
- Narrowing of dialysis fistula grafts. Happens very often in hemodialysis patients, leads to reduced blood flow and is the cause of inadequate hemodialysis.
Percutaneous angioplasty is vascular stenting and is a minimally invasive procedure designed to improve blood flow in the body's arteries.
In angioplasty, guides and catheters are used, ending with a balloon at their tip representing a thin plastic tube. These reach the site of narrowing or blockage of the vessel. The balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated with a special inflation syringe, then dropped again and removed.
Angioplasty is only one method of treating narrowing and blockage of the arteries. Drug therapy is the first step.
For more information, you can call +359895770869.