What is Crohn's disease?
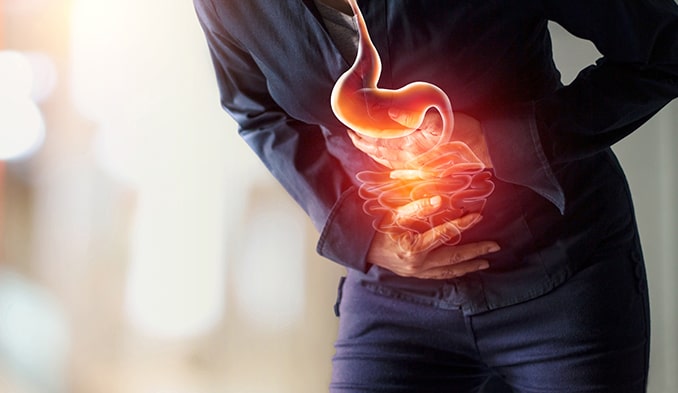
Crohn's disease is an autoimmune, chronic disease that causes inflammation in the digestive system. It can affect any part of the digestive tract - from the mouth to the anus, most commonly affecting the small intestine and the beginning of the colon. It is also called 'regional enteritis'. Dr. Burrill Crohn first described the disease in 1932.
Reasons
The exact cause of the disease has not yet been determined. Predisposing factors are:
- Family history - people who have one parent with Crohn's disease have a 7% to 9% risk of developing the disease, while people with two parents with Crohn's disease have a 35% risk;
- Age - more common in young people - between 20-30 years of age;
- Smoking - may increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease;
- Medicines - drugs such as antibiotics, birth control pills and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can increase the chance of developing the disease;
Symptoms
Symptoms in Crohn's disease can range from mild to severe. They usually develop gradually, but can also occur suddenly. These symptoms can be:
- Fatigue;
- Abdominal pain;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Cramps;
- Blood in the passages;
- Diarrhea that lasts more than 2 weeks;
- Decreased appetite and weight loss;
Crohn's disease can cause other problems, including:
- Loss of appetite and weight loss;
- Anemia;
- Bowel obstruction (intestinal obstruction);
- Fistulas;
- Abscesses;
- Anal fissures;
- Ulcers, open sores in the mouth, intestine, anus or perineum;
- Inflammation in other areas of the body - joints, eyes and skin;
How is Crohn's disease diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made by:
- Colonoscopy;
- Gastroscopy;
- Biopsy;
- Computed tomography; magnetic resonance imaging;
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease are inflammatory bowel diseases. It is important to distinguish between these conditions as there are different treatments.
Similarities
- Stomach cramps and pain;
- Diarrhea;
- Constipated;
- Rectal bleeding;
- Loss of appetite;
- Weight loss;
- Fatigue;
- It is diagnosed with colonoscopy;
Differences
Although there are similarities between Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, key differences distinguish these conditions and require different treatment approaches. The differences are:
- Ulcerative colitis develops only in the colon, whereas Crohn's disease can develop anywhere in the digestive tract;
- Ulcerative colitis causes constant inflammation throughout the colon, whereas Crohn's disease causes intermittent inflammation around healthy tissue;
- In ulcerative colitis, rectal bleeding is more common;
- Mouth sores, infections and bowel stenosis are more common in Crohn's disease;
Treatment
Treatment methods for Crohn's disease are aimed at relieving symptoms.
- Adherence to diet - avoid foods and drinks that intensify complaints;
- Individual approach to each patient;
- Medication treatment;
- Surgical treatment - recommended in cases when medical treatment does not work.