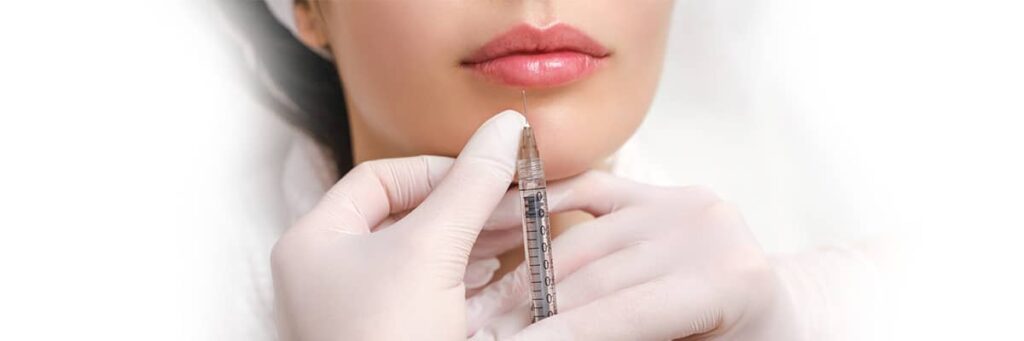
The placement of injectable fillers with collagen or fat to augment soft tissue is a cosmetic procedure. It is performed to correct wrinkles, depressions in the skin or scars. The procedure involves injecting a substance (collagen and/or fat) into the skin to fill in the treated area.
The result of the procedure is usually not permanent and corrective injections may be needed every 3 to 12 months. For some, however, collagen injections can stimulate the body's own collagen production, extending the time needed between subsequent injections.
What is injectable collagen (injectable collagen fillers)?
It is designed to stimulate the body's natural production of collagen, a protein that gives skin its structure and elasticity. Collagen-stimulating fillers are made of calcium hydroxyapatite or poly-L-lactic acid, which are injected into the skin to trigger collagen production. This protein provides structure to the skin, bones, ligaments and other parts of the body. Collagen fillers are commonly used to treat wrinkles, scars and facial lines. They can be used almost anywhere on the face and are especially helpful for the jawline. The results of collagen boosting fillers are gradual and may take a few weeks to appear, but can last up to two years. The results usually appear natural as they are achieved through the skin's own production of collagen. Approximately 97% of patients have experienced no adverse reactions.
What is injectable fat (injectable fat fillers)?
Injecting your own fat to correct skin blemishes is called microlipoinjection. This involves transferring or recycling fat from one area of the body to another, allowing the surgeon to recontour the skin. With a small needle, the fat is extracted and then re-injected into the chosen site. Injectable fat fillers are often a preferred treatment choice as it involves the use of your own fat, reducing the risk of allergic reactions. Fat transfer offers a longer lasting result than fillers. Fat transfer has the potential to offer lasting or near-lasting improvement in many patients.
Possible complications
Allergic reaction to collagen is a possible complication of collagen treatment. Therefore, to avoid an allergic reaction, tests are done to determine if the patient is allergic to collagen.